E
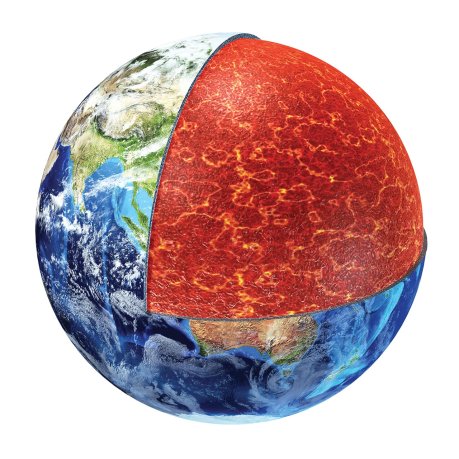
Earth mantle
The predominantly solid interior of the Earth lying between the crust and the liquid outer core. The mantle occupies about 84 percent of the Earth’s total volume and is made up mostly of hot silica rocks. Its consistency is somewhat reminiscent of caramel; it is viscous and moves slowly (over millions of years). The lighter parts, heated from the Earth’s core, rise upwards, while the heavier parts sink downwards. Sites in the Earth’s crust above upward plumes in the mantle are areas of high tectonic activity and are suitable for geothermal energy exploitation. The gradual movement of rocks in the Earth’s mantle drives plate tectonics and shapes the form of continents.